
Power over Ethernet (PoE) Explained: Types, Uses, and Key Benefits
What is power over ethernet?
The technology known as Power over Ethernet (PoE) allows wired Ethernet local area networks (LANs) to be implemented by using Ethernet data cables rather than conventional electrical power cords and wiring to carry the electrical current required to run each device.
PoE, which is utilised in both business and smart home settings, replaces electrical cable, which only provides power and necessitates separate data wiring, with less expensive Ethernet cabling that can carry both data and power. PoE allows electrical wire to stay intact and requires less wiring because it uses Ethernet connection to carry both power and data.
What are power over ethernet devices?
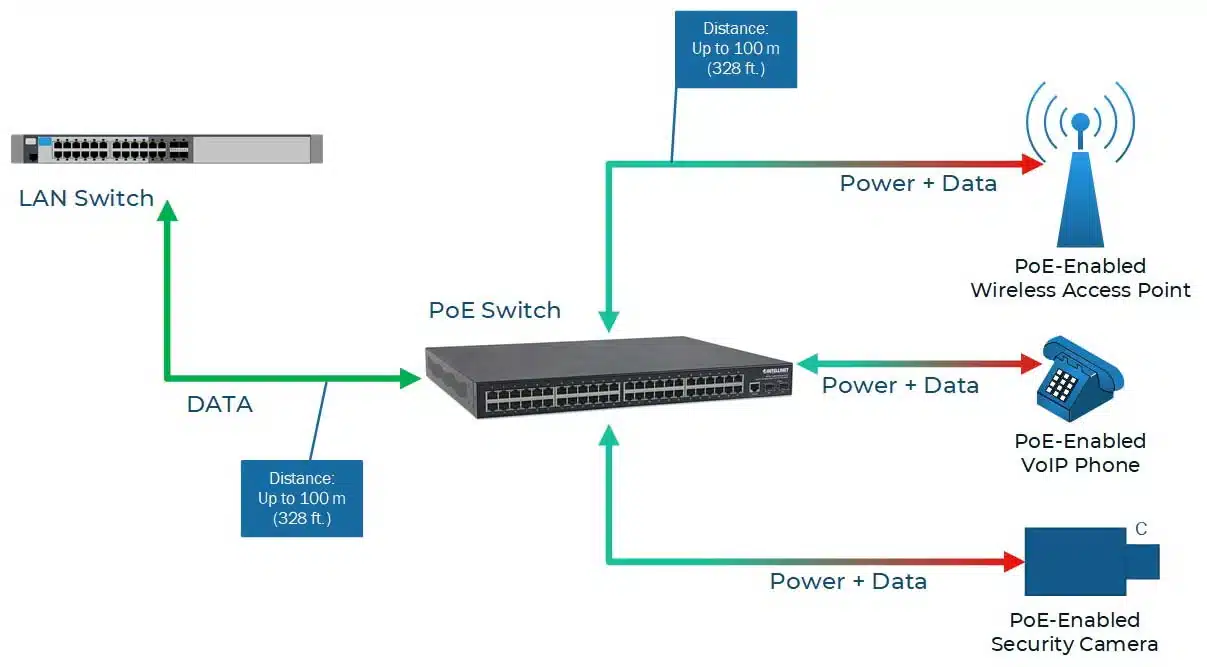
Power over Ethernet (PoE) devices are network-enabled devices that do not require separate power outlets or cords because they can receive both data and electrical power through a single Ethernet cable. This technology makes installation easier by enabling devices to be installed anywhere a network cable can reach, such as VoIP phones, wireless access points, and security camera.

Power over Ethernet (PoE): Types and Standards
Based on their power levels and standards, PoE equipment can be divided into four categories. However, keep in mind that the power received by PD will typically differ from the maximum power output of the PSE due to power loss via cable distance.
PoE (IEEE 802.3af)
The IEEE first proposed this PoE standard in 2003. It has a maximum power output of 15.4W (watts), although the linked PDs usually receive 12.95W.
PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at)
2009 saw the certification of PoE+, which provides a major improvement in power delivery. It can provide up to 30W of electricity, but PDs usually only receive about 25.5W of power.
Type 3 PoE++ (IEEE 802.3bt)
The PoE++ technology known as Type 3 (IEEE 802.3bt) was standardised in 2018. It provides up to 60W of power, of which about 51W is received by PDs.
Type 4 PoE++ (IEEE 802.3bt)
It is the most recent standard, Type 4 PoE++. Despite being introduced in the same year as type 3, this version has a higher power output of up to 100W, whereas the PDs will only receive about 71.3W after cable dissipation.
Additionally, type 3 and type 4 PoE++ use the more current 4-pair arrangement, which uses all four wire pairs in the Ethernet connection for simultaneous data and power transfer, resulting in increased power delivery. The older endspan and midspan designs are adaptable to current devices since they require two wire pairs for power delivery and two for data transfer.
What is power over ethernet used for?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) simplifies network installations by powering wireless access points, security cameras, IP phones, retail Point of Sale (PoS) terminals, building access systems, PA systems, LED lights, VDI terminals and digital signage with a single Ethernet cable.
Powering wireless access points (APs) is usually PoE. This eliminates endpoint power concerns and simplifies installation in suitable locations.
Security Cameras: PoE powers security cameras, allowing for greater positioning and cheaper installation. Large facilities without conventional power sources benefit from this.
Office IP phones are often powered by PoE. This centralises power control and eliminates power adapters.
PoE powers retail Point of Sale (PoS) terminals, simplifying checkout and eliminating the need for multiple power sources.
Building Access Terminals: PoE-powered access control systems simplify building security administration.
PoE powers PA systems in several places, eliminating the need for separate power sources and simplifying installation.
LED Lighting: PoE powers LED lighting systems, notably smart building ones. This allows central lighting control and power management.
Digital Signage and VDI Terminals: PoE powers digital signage and VDI terminals, simplifying installation and cutting expenses.
How to Choose the Right POE Standard According to Voltage and Wattage
Power over Ethernet voltage is usually 35V to 57V, depending on needs. According to IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) regulations, this voltage level is SELV (Safety Extra Low Voltage), meaning electrical shocks are rare under normal operating settings.
PoE technology also protects PDs with the handshake protocol. Before powering the PD, the PSE sends a low voltage to establish its power needs. If successful, the PSE will power the PD. The PSE will cease power distribution if the handshake fails for whatever reason, preventing damage or accidental activation.
Remember that the low voltage handshake protocol and SELV designation do not completely safeguard against electrical hazards. A 48V PoE current could shock someone like a 9-volt battery, however it’s unlikely. Avoiding PoE misuse and doing hardware inspections are essential for safety. PoE-powered gadgets demand varying quantities of electricity like other electronics. By knowing the PDs’ power needs, users can choose a PSE with enough PoE wattage to avoid gearbox issues.
The following table provides a quick overview of each PoE type’s characteristics and supported applications:
| PoE Name | PoE | PoE+ | Type 3 PoE++ | Type 4 PoE++ |
| PoE Standard | IEEE 802.3af | IEEE 802.3at | IEEE 802.3bt | IEEE 802.3bt |
| Max. Power Output | 15.40 W | 30 W | 60 W | 100 W |
| Power to PD | 12.95 W | 25.5 W | 51 W | 71.3 W |
| Voltage Range | 44V to 57V | 50V to 57V | 50V to 57V | 52V to 57V |
| Pins Required | 4-pins / 2-pairs | 4-pins / 2-pairs | 8-pins / 4 pairs | 8-pins / 4 pairs |
| Configuration Type | Endspan, Midspan | Endspan, Midspan | Endspan, Midspan, 4-pair | Endspan, Midspan, 4-pair |
| Supported Applications | Static security cameras, VoIP devices, wireless access points, etc. | PTZ security cameras, security alarms, video IP phones, etc. | Video conference devices, wireless multi-radio access points, etc. | Advanced video conference devices, digital signage displays, etc. |
Power over Ethernet: Benefits and Drawbacks
What are the benefits of Power over Ethernet (PoE)?
Simplify network installation and lower costs by doing away with the need for separate DC power sources and data lines.
Permit network devices to be positioned in areas with difficult access to outlets, giving users flexibility in device placement.
Facilitate remote device management, monitoring, and control, which eases network upkeep and troubleshooting.
Ensure compatibility and standardisation by adhering to universal standards.
A dependable and secure DC supply solution for data network applications.
What are the drawbacks of Power over Ethernet (PoE)?
POE technology may be more expensive to adopt since it requires more hardware, like POE switches or injectors.
For bigger network installations, POE technology might not be appropriate because of the possibility of energy loss over greater distances.
POE-powered devices may have slower network millisecond (ms) rates than devices powered by conventional DC power sources because of certain constraints.
Using POE technology can be more expensive than using typical DC techniques, particularly if you need to modify your current network equipment.
How Does Power over Ethernet Work?
Electrical current must enter an Ethernet data connection from the power source end and exit at the device end for PoE to function. Ethernet makes it possible to keep the data signal and power current apart so that neither disrupts the other. Through a part known as an injector, current enters the Ethernet wire. It will operate correctly without any changes if the device at the other end of the cable is PoE-compatible. A picker, sometimes known as a tap, must be inserted in order to remove the current from the cable if it is not PoE-compatible. The power outlet receives this picked-off current.
FAQ
Can PoE deliver an Uninterruptable Power Supply?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) does not inherently provide an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). However, if the PoE switch or injector is connected to a UPS, it can deliver uninterrupted power to the connected devices during a power outage. This setup can help ensure the continuous operation of critical devices.
Is PoE useful in extending network reach?
Absolutely! PoE technology can significantly extend your network reach. By delivering DC and data over the same Ethernet cable, you can install devices like security cameras or wireless access points in locations far from DC outlets. This makes PoE ideal for large-scale and flexible network deployments.











