
Motherboard Sizes Explained: A Complete Guide to the Different Types
Motherboards are the most important part of any computer because they are the base for all computer systems. The motherboard is the main part of your PC that connects all the other parts. Its features and specifications have a direct effect on how powerful and efficient your PC can be. No matter if you’re building a new computer or upgrading an old one, you should know about the different sizes of computer motherboards, from ATX to Mini-ITX.
In this guide, we’ll look at the many sizes and types of motherboards that are out there. This will provide you the information you need to make a smart choice for your next project.
Different Types of Motherboards
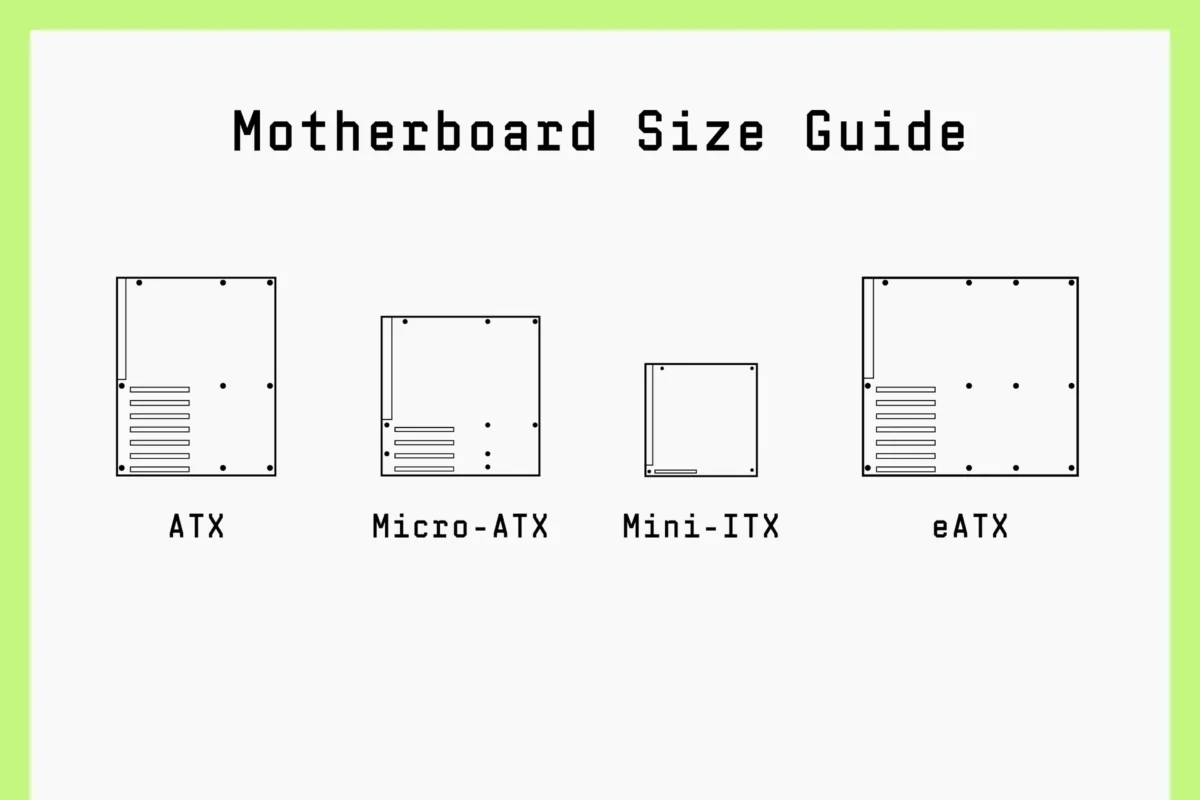
The size of a motherboard directly relates to its type. Below, we will walk you through the most common motherboard form factors and their typical dimensions.
Motherboard Sizes at a Glance
| Motherboard Type | Standard Size |
| ATX | 305mm x 244mm |
| Micro-ATX | 244mm x 244mm |
| Mini-ITX | 170mm x 170mm |
Note:There isn’t a formal industry standard for E-ATX motherboards. The size can change from one model to the next, therefore it’s always best to look at the specs of a certain E-ATX board before buying it.
ATX Motherboards
- Size and Design: ATX boards are 305mm x 244mm, which gives you enough of area for high-performance setups. Their bigger design helps with ventilation and cooling.
- Expansion Capabilities: Most of these include 4 to 7 PCIe slots, which lets you add more GPUs, sound cards, network adapters, and other expansion devices. This makes them great for gaming, content creation, and workstation configurations.
- Memory and Storage: Most ATX models have four or more RAM slots for dual- or quad-channel memory, as well as several SATA and M.2 ports for a lot of storage space.
- Connectivity and Features: Expect a lot of connectors, such USB 3.x, Thunderbolt, and high-speed Ethernet. There are also extras like Wi-Fi, RGB lighting, and smart fan control, which are great for gamers and fans who want to customize their setup.
Micro-ATX Motherboards
- Compact Size: Micro-ATX boards are smaller than ATX boards but bigger than Mini-ITX boards. They are 244mm x 244mm, which is a good size for both smallness and usefulness.
- Expansion Slots: They have 2 to 4 PCIe slots, which can hold one GPU and a few add-on cards. This is enough for most gaming and everyday computer demands.
- Memory Support: Many Micro-ATX boards, like ATX boards, can hold up to four RAM sticks for good performance.
- Affordability: They are often less expensive than ATX, which makes them appealing to builders who wish to be able to expand their systems without spending a lot of money.
Mini-ITX Motherboards
- Ultra-Compact Design: Mini-ITX boards are only 170mm x 170mm, so they fit in compact cases and save room when building.
- Limited Expansion: They usually only have one PCIe slot, which is commonly used for a graphics card, so they can’t add on to them, but they are still good enough for many setups.
- Memory and Storage: Most include two RAM slots and a small number of SATA and M.2 ports because there isn’t enough room for more.
- Specialized Use: Great for HTPCs, small gaming rigs, or systems that can be moved around. Many Mini-ITX boards still have features like built-in Wi-Fi, decent audio, and efficient cooling, even if they are small.
There are pros and cons to each motherboard size, and they are made for different types of users. ATX boards are great for performance and expandability, Micro-ATX boards are a good mix between size and affordability, and Mini-ITX boards are great for small, portable setups. It all depends on what you want in terms of size, performance, and future improvements.
MicroATX vs. Mini-ITX: Pros and Cons

These different types of motherboards, starting with Mini-ITX, cost more than the cheap microATX ones. The prices of mini-ITX and microATX models from major brands are about the same these days.
The ASRock A620I Lightning Wi-Fi ($139.99), Gigabyte B850I Aorus Pro ($279.99), and MSI MPG B650I Edge WiFi ($299.99) show that Mini-ITX Socket AM5 options are more expensive. The ASRock B650M Pro RS ($139.99), the MSI Pro B650M-A Wi-Fi ($159.99), and the Gigabyte B850M Gaming X Wi-Fi 6E ($179.99) are all MicroATX options that cost less than $200.
Mini-ITX and MicroATX motherboards have different numbers of ports and connections, in addition to their size and price. Mini-ITX motherboards are small, measuring only 6.7 × 6.7 inches. They have one PCIe x16 graphics card socket and two M.2 SSD connectors. The manufacturer might only give you two RAM slots instead of four, and the back I/O might be limited, which means there will be fewer USB ports and other connections.
MicroATX motherboards usually have four RAM slots, two PCIe x16 slots, up to four M.2 ports, and more rear I/O options because they have 43% more space than standard ATX motherboards. MicroATX is cheaper and has more features, but it’s also bigger, which makes small form factor (SFF) builds less sleek and compact and more durable. Would you need more than two M.2 ports, a graphics card slot, and basic rear I/O? Silicon might need to be bigger.
ATX vs. E-ATX: pros and cons
ATX and E-ATX look about the same when compared to the two smaller motherboard sizes. The 35% increase in space can be very impressive, depending on the technology used. A standard ATX motherboard has four PCIe x16 ports and four RAM slots. E-ATX motherboards can have eight ports and eight RAM slots, but this is not likely to happen by 2025.
E-ATX motherboards cost more and are harder to find than ATX motherboards. The motherboard has extra space for components, but that will cost you more. It works with AM5 and LGA 1851 sockets. The ASRock X670E Taichi ($449.99) and MSI MEG X670E ACE ($499.99) are two popular E-ATX options that cost less than ATX. The ASRock X670E Steel Legend ($259.99) and the MSI MAG X670E Tomahawk Wi-Fi ($239.99) are ATX models that cost less.
You might want to pay twice or more for an ATX motherboard because it has more space. It depends on how it is used. Power users will benefit from the larger board surface, which is important for building a high-end gaming PC with a custom loop in a bigger E-ATX-compatible PC box with the latest parts. E-ATX gives you the most space and airflow if you can afford it.
People often say that the extra data lanes on E-ATX motherboards don’t help gaming. But people who are making a server, a deep-learning machine, or something else that needs more detail may need the extra slots and connections. Want more slots for expansion? If this is the case, E-ATX might be a good choice. If not, ATX will work for almost any job and is cheaper and easier to find.
Conclusion: Which Motherboard Should You Buy?
Choosing the right motherboard isn’t just about size; you also need to think about your budget, build goals, and the parts you want to use. In 2025, builders will be able to choose from ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX, and E-ATX, each of which has its own strengths. Mini-ITX boards make for sleek, small builds, but they usually cost more. Micro-ATX boards are a good middle ground because they have fewer features and are less expensive. ATX is still the most popular choice because it can be expanded and is easy to find. E-ATX is better for people who want to build high-end workstations or servers.
Most importantly, compatibility is key. Make sure your motherboard can handle the CPU, GPU, memory, and storage you want to use, whether you choose AMD’s AM5 or Intel’s newest LGA 1851 socket. PCPartPicker and other tools like it are great for making sure that parts will work together and for seeing what your system will look like before you buy it.
Think about how big your case needs to be, how fast it needs to be, and how much room you want to add more parts. Your motherboard is the most important part of your computer. It sets the stage for everything else. Choose one that fits your vision and your plans for the future.
FAQ
What size of motherboard should I get?
The size of the motherboard you need depends on the size of your case and what you want to build. An ATX board is the best choice if you have a big PC case and need a lot of slots for GPUs, RAM, and other cards. Micro-ATX or Mini-ITX boards are better for smaller setups like HTPCs or small gaming PCs. Always think about the space you have and the parts you want to put in.
Are all motherboards the same size?
No, motherboards come in a variety of shapes and sizes. ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX are some of the most common ones. There are also other options, such as E-ATX or Nano-ITX. Since each one has its own size and purpose, you should choose one that fits your system’s case size and performance needs.
Why is the size of the motherboard important?
The size of the motherboard affects how well it fits in a case, how many expansion slots it has, and the overall design of the system. Larger boards, like ATX, have more features and can be expanded, but they need bigger cases. Mini-ITX and other small boards save space, but they don’t let you add as many things. Your choice should be based on your goals for the build, the space you have, and how well it needs to work.
How do I find out what size my motherboard is?
To find out what size your motherboard is, measure its length and width and then compare those numbers to standard form factors like ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. Another easy way is to look up the model number of the motherboard online. There, you will find the exact size and specifications.











