
A Complete Guide to Mini-ITX Motherboards: Size, Applications, Pros & Cons
Compact, high-performance computing technologies are now popular with both consumers and businesses. The Mini-ITX motherboard is the center of this trend because it strikes a good balance between performance, energy efficiency, and size. Mini-ITX now includes gaming consoles, home NAS systems, industrial control devices, kiosks, digital signage, and AI edge computing devices, in addition to HTPCs and small desktops.
Mini-ITX motherboards let PC fans build powerful gaming or office computers in smaller cases, which strikes a balance between performance and space. Retail, banking, smart cities, and industrial control companies use Mini ITX motherboards, especially ARM-based and Thin versions, for embedded devices and terminals that run all the time.
This article looks at Mini-ITX motherboards in depth, covering their definitions, size standards, possible uses, advantages and disadvantages, the best 2025 buying suggestions, and market trends. Readers learn how useful and versatile this small motherboard standard is.
What is Mini-ITX Motherboard?
First released by VIA Technologies in 2001, the Mini-ITX motherboard is a typical small motherboard that measures only 170 x 170 mm. Mini-ITX supports CPUs, memory, storage interfaces, and expansion slots, and it takes up less space than ATX (305mm × 244mm) or Micro-ATX (244mm × 244mm) setups.
Mini-ITX motherboards are small, built-in, and use less power. They work well with PCs and are the main platform for small and industrial devices. The Thin Mini-ITX is a similar model that is 170 x 170 mm and 25 mm thick. It also has an external DC power supply connector. This is why it is so popular in digital signage, self-service kiosks, embedded computers, and industrial tablets.
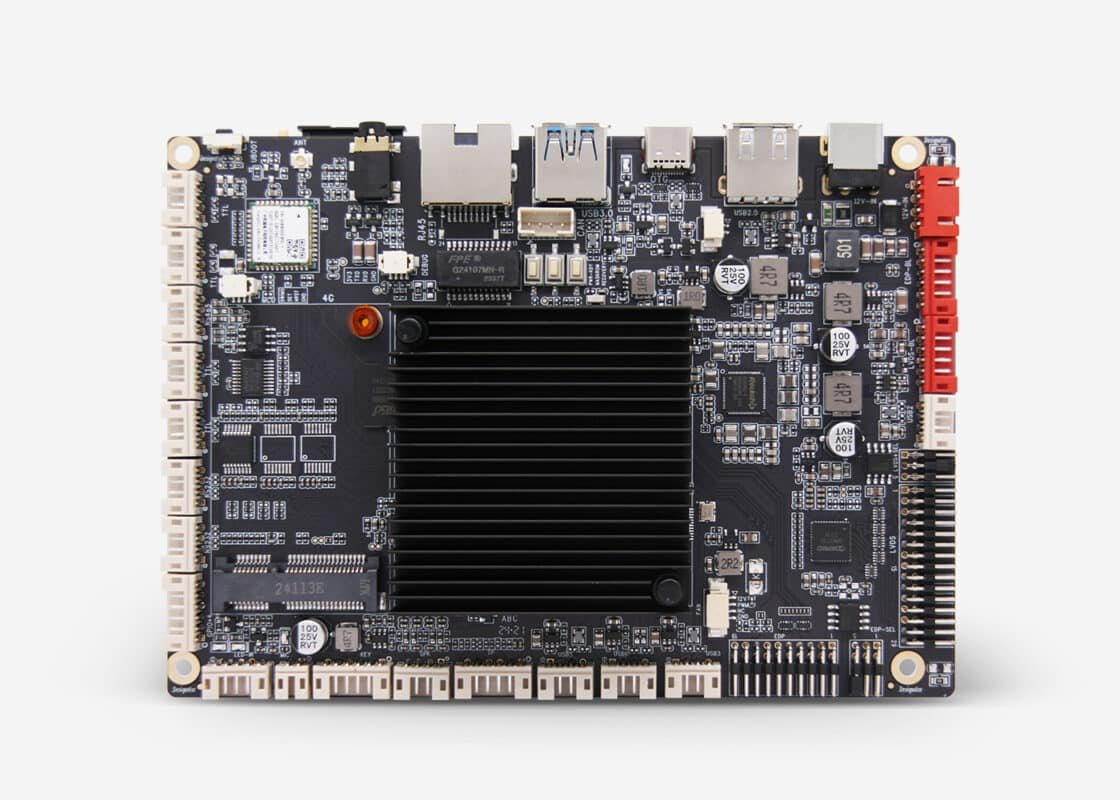
Application Scenarios for Mini-ITX Motherboards
Mini-ITX motherboards are widely used in both consumer and industrial applications due to their compact size, energy efficiency, and high integration.
- Gaming Mini PC: Packing high-performance CPUs and graphics cards into compact cases to create powerful machines;
- HTPC Home Theater: Low-noise playback of 4K video and streaming media;
- NAS Network Storage: Multiple SATA interfaces and low-power design, ideal for home and SOHO data centers.
In the industrial and commercial markets, Mini-ITX—particularly ARM-based and Thin Mini-ITX—are widely used in:
- Applications of ARM Mini-ITX in AIoT and Edge Computing
As AI and IoT get better, ARM-based Mini-ITX motherboards are quickly making their way into new markets like smart gateways, edge servers, and AI inference terminals. The ARM architecture is great for digital signage, smart security, and smart retail because it uses little power, keeps costs down, and runs smoothly.
- Kiosk and POS Systems
Thin Mini-ITX motherboards are now the most popular choice for things like self-service ordering kiosks, payment terminals, and bank teller machines because they are thinner and have a DC power input. They can run touchscreens and payment modules while still being able to work 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
- Industrial Control and Embedded Devices: Factory Automation, Healthcare, Transportation.
ARM Mini-ITX vs AMD/Intel Mini-ITX
ARM Mini itx focuses on power efficiency for embedded systems, while AMD and Intel mini itx focus on high-speed computing. Intel sometimes has better single-thread performance, and AMD sometimes has better integrated graphics.
When it comes to low-power embedded applications, ARM boards often give you more bang for your buck.
For some tasks, ARM systems may need more specific operating systems and drivers. On the other hand, AMD and Intel platforms work with a wider range of software and hardware for common operating systems and applications.
ARM boards are best for embedded systems, while AMD and Intel boards are better for high-end PCs and servers.
Best Mini-ITX Motherboard Recommendations for 2025
As we move into 2025, Mini itx motherboards are more varied and meet the needs of both businesses and consumers.
Thin Mini-ITX boards are widely used in kiosks, self-service payment terminals, and digital signage in businesses and factories because they are thin and have DC power supply benefits. At the same time, ARM Mini-ITX motherboards are becoming more popular because they use less power and work with AIoT, making them good choices for smart retail, edge computing, and industrial control applications.
AMD B650I and Intel Z790I motherboards are still popular among gamers. They support the newest processors and high-frequency DDR5 memory, so they can deliver top performance even in small cases. ITX motherboards with two Ethernet ports and several SATA/M.2 interfaces, like those from ASRock and Synology, are popular among home and small office NAS users. These boards strike a balance between storage scalability and low power consumption.
The 2025 Mini-ITX motherboard market has something for everyone, whether you’re a performance enthusiast or a business setting up a lot of terminals.
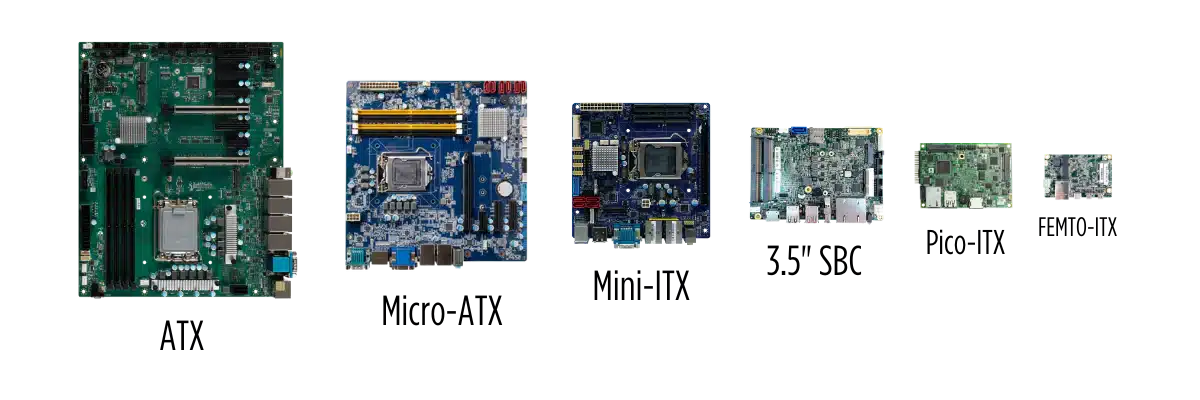

Advantages and Limitations of Mini-ITX Motherboards
The best thing about Mini ITX motherboards is that they are small and save space, which makes them perfect for situations where there isn’t much room on the desk or where embedded solutions are needed. They also work with most CPUs and graphics cards, which means they can handle a lot of power in small cases. They are also more energy-efficient and quieter than larger boards, which makes them good for environments where there aren’t any fans or where they need to run all the time. In addition, Mini-ITX has become very popular, with a fairly well-developed ecosystem of cases, coolers, and other parts.
Limitations come mostly from the fact that the device can’t be expanded enough. It usually only has one PCIe slot, two memory slots, and a small number of ports. Space limits also make it harder to manage heat, since high-performance hardware tends to build up heat in small cases. Also, Mini-ITX motherboards are often more expensive than similar ATX models, which means they don’t always give users the best value for their money.
So, when choosing a Mini-ITX motherboard, you need to think about performance, expandability, and how much space it needs.
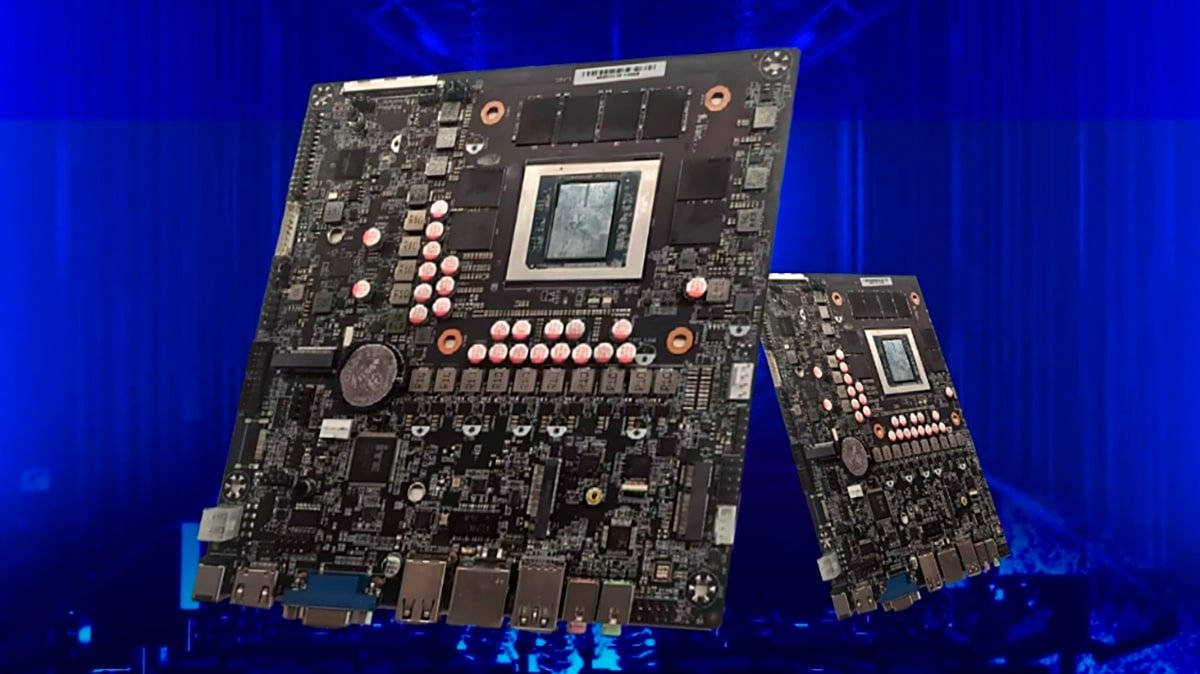
How to Choose a Good Mini-ITX Motherboard
When choosing a Mini-ITX motherboard, you should think about how you plan to use it and whether it will work with your other hardware. First, think about the platform for the CPU: Intel Z-series or AMD B-series ITX motherboards are better for high-performance gaming or workstations. ARM architecture motherboards are better for low-power consumption and AIoT applications.
Next, put memory and the ability to add more memory at the top of your list. Most Mini-ITX boards only have two memory slots, so NAS or industrial devices need to have the most memory and support for ECC memory. At the same time, make sure there are enough SATA ports, M.2 slots, and PCIe lanes for graphics cards, SSDs, or network expansion.
Designing the network and the power are both very important. Some motherboards have 2.5G/10G Ethernet ports or two network ports built in. This is very useful for server and edge computing. Because they have DC power connectors, thin Mini-ITX boards are better for all-in-one PCs and kiosk devices.
Lastly, don’t forget about managing heat and making sure the chassis fits. To make sure that compact chassis work reliably for a long time, they need well-designed airflow paths or fanless solutions.
Conclusion: Market Trends and Future Outlook
Mini-ITX motherboards have been driven by the computing industry’s desire for low power consumption, high performance, and downsizing. In the consumer sector, its small size and good performance appeal to do-it-yourselfers, home theater enthusiasts, and office workers. Its stability and scalability are utilized in commercial and industrial settings by digital signage, point-of-sale systems, edge computing, and automation control.
Wi-Fi 7, USB4, PCIe 5.0/6.0, and DDR5 will all gain traction eventually. With ARM architecture, AI chips, and energy-efficient processors, mini-ITX motherboards will combine performance and energy efficiency. These gadgets will help develop AIoT, smart terminals, and green computing by surpassing temperature and expansion constraints.
The interface number and heat management space limitations prevent them from outperforming ATX motherboards in extreme performance. Nonetheless, the “small yet powerful” design of Mini-ITX motherboards satisfies both current and future computing demands. A more flexible, intelligent, and sustainable future is made possible by these hardware form factor innovations, which are also a major force behind intelligent and multi-scenario applications.
FAQ
What is the size of a Mini-ITX motherboard?
A Mini-ITX motherboard has a standard size of 170mm× 170mm, making it smaller than ATX and Micro-ATX boards, ideal for compact PC builds.
What is the difference between Mini-ITX and Thin Mini-ITX?
Thin Mini-ITX maintains the same 170mm×170mm footprint but is thinner (around 25mm) and often uses external DC power, making it suitable for embedded systems, kiosks, and all-in-one PCs.
Is a Mini-ITX motherboard good for gaming?
Yes, Mini-ITX motherboards can support high-performance CPUs and graphics cards, making them suitable for compact gaming PCs, though expansion options are more limited compared to ATX boards.
Can a Mini-ITX motherboard be used for NAS?
Yes, Mini-ITX motherboards with multiple SATA ports and network interfaces are ideal for small home or office NAS setups, offering low power consumption and reliable 24/7 operation.
What is an ARM Mini-ITX motherboard used for?
ARM Mini-ITX motherboards are commonly used in embedded systems, edge computing, digital signage, IoT devices, and industrial applications where low power consumption and compact size are critical.











